1. 基本概念
首先事务并不是Spring的概念,也不是Java-EE的概念,所有的事务管理器都具有如下属性。可以理解定义一套通用的事务实现协议。
1.1 事务的传播性 – 新事务与当前事务关系
传播性(propagation) – 描述了新事务与当前事务的关系,比如说当方法如果两个都处于事务中,调用时候根据不同定义会有不同的行为
常见的如下六种:
| 传播定义 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| REQUIRED | 如果当前没有事务则创建一个新的事务,否则则沿用 |
| SUPPORTS | 支持当前事务, 如果没有则在无事务环境下执行 |
| MANDATORY | 可以沿用当前事务,但如果不存在则报错,与required的不同是: 强制当前一定要有事务存在 |
| REQUIRES_NEW | 强制创建一个新的事务,并且中断(suspend)当前已经存在的 |
| NOT_SUPPORTED | 在无事务环境中执行,如果当前已有则会直接中断(suspend) |
| NEVER | 需要在无事务环境中执行,如果有则直接抛异常 |
1.2 事务的隔离性 – 不同事务操作的影响程度
隔离级别(isolation) – 比如说没有被提交的操作是否可以被看见。这个特性主要是界定 与数据库层面打交道时的特性,不过也只是通用定义,因为并不是所有数据库都支持的。
1.3 超时
如果一个事务多久没有执行完成,就应该被取消。如果在某个事务中执行了耗时的操作,需要考虑设置适当的超时时间
注意这个超时是与底层事务系统有关的,比如说如果使用的是MySQL数据库,这个超时就应该至少大于等于MySQL数据库底层的超时时间
Many resources or resource drivers will not support this, but both the JTA API (though not all implementations) and various JDBC drivers do
2. Spring中的事务机制
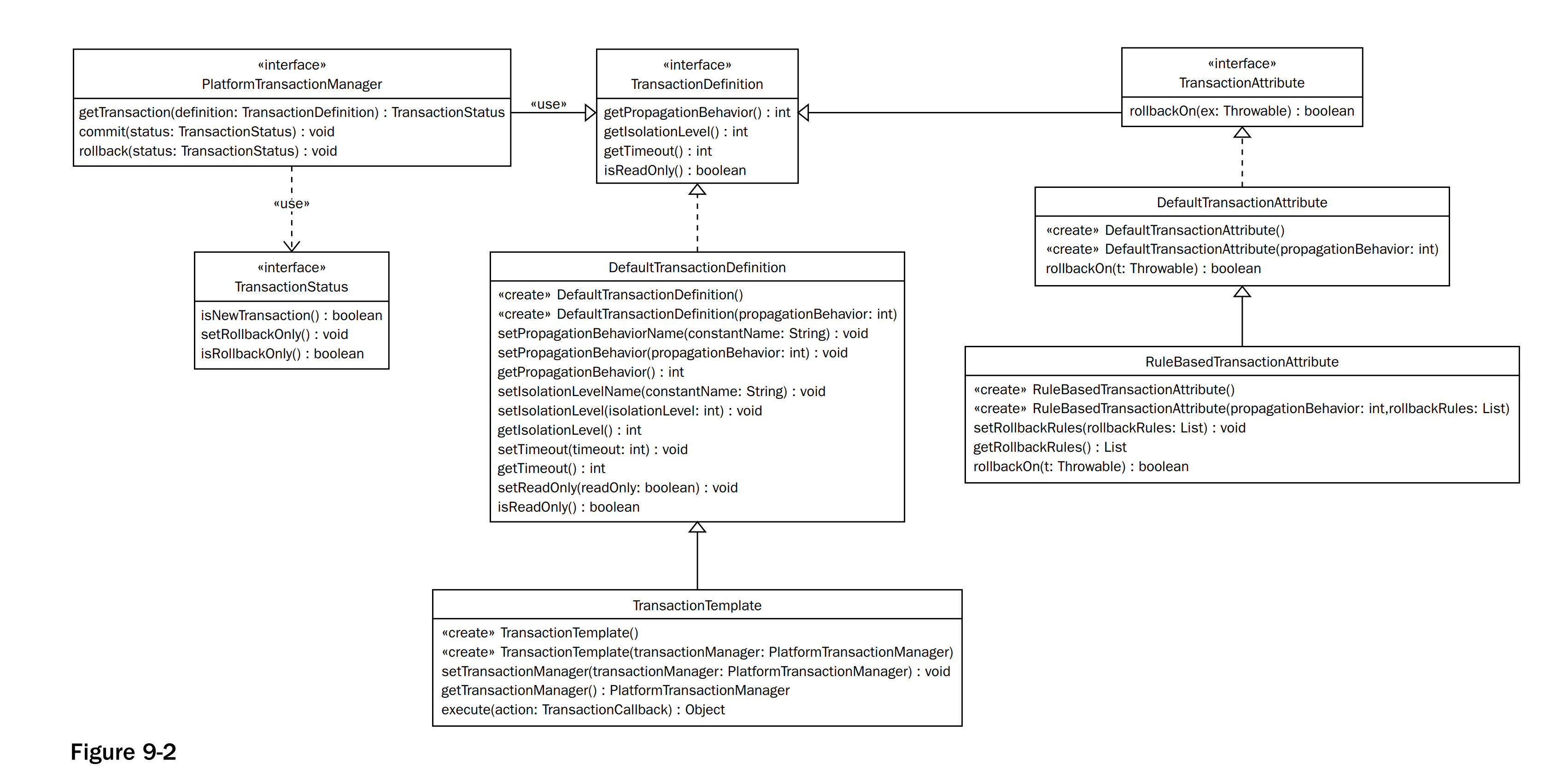
Spring事务机制的抽象就是PlatformTransactionManager, 它有如下几个重要的的属性:
Regardless of whether you opt for declarative or programmatic transaction management in Spring, defining the correct PlatformTransactionManager implementation is absolutely essential. You typically define this implementation through dependency injection.
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException
}
- getTransaction
根据当前的事务定义返回事务状态, 通过会在子类中,实现获取事务的方法, 如AbstractPlatformTransactionManager中的定义的doGetTransaction()
- rollback
根据上一个方法返回的事务状态,来决定当前事务是需要提交还是需要回滚
通常情况下,我们不会直接使用该接口,而是继承AbstractPlatformTransactionManager, 比如说比较常见的DataSourceTransactionManager。当然底层依然是比较通过AutoConfiguration来引入的, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration。
2.1 编程式事务(Programmatic TxManagement)
2.2 声明式事务(Declarative TxManagement)
Most users prefer declarative transaction management, which is recommended in most cases.
通过AOP Proxy实现
The previous section outlined the basics of how to specify transactional settings for classes, typically service layer classes, declaratively in your application
上一部分简单介绍了如何配置声明式事务(一般是在Service层)
the recommended way to indicate to (Spring Framework’s transaction infrastructure that a transaction’s work is to be rolled back) is to throw an Exception from code that is currently executing in the context of a transaction
告知Spring事务管理器某个事务是否应该被回滚的建议方式就是 在事务的执行代码中抛出异常然后由Spring来决定是否回滚。
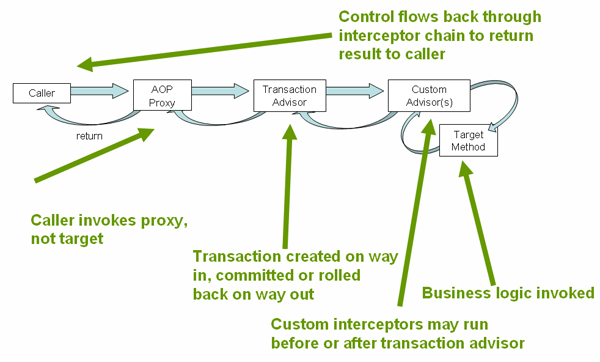
In proxy mode (which is the default), only external method calls coming in through the proxy are intercepted; This means that self-invocation (in effect, a method within the target object calling another method of the target object) does not lead to an actual transaction at runtime even if the invoked method is marked with @Transactional
注意,默认情况下事务的创建是通过外部调用方法被AOP Interceptor拦截,从而导致了相应事务的创建。所以,如果在Service内部调用被@Transactional修饰的方法,是不会生效的(也就是对this.xx无效)。
如果想要内部调用的事务也生效,需要使用AspectJ mode
@Transactional
public void xx() {
}
public void yy() {
xx();
}
使用@Transactional注解
org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagementSpring基于注解的事务管理器的实现
Sopped at Method visibility and @Transactional
@Transactional注解解析实现: org.springframework.transaction.annotation.SpringTransactionAnnotationParser。
而默认的实现是基于规则的: org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.RuleBasedTransactionAttribute
3. 事务的执行流程
假设Spring boot中使用DataSourceTransactionManager,以一个简单用户详情查询/user/{id}, 然后UserSevice根据ID去数据库查询相应的用户为例梳理整个流程。
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends GenericServiceImpl<User, Integer, UserMapper> implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public UserMapper getGenericMapper() {
return userMapper;
}
// 根据Mybatis-generator生成的模板方法
@Override
@Transactional
public User selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id) {
return super.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
}
@RequestMapping("/user")
@RestController
public class UserController {
private final UserService userService;
@Override
public WebApiResponse<User> detail(Integer id) {
User user = userService.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
}
3.1 DataSourceTransactionManager – 基于数据源的事务管理器
PlatformTransactionManager: Spring中事务管理器,定义与事务相关的核心方法,获取、提交和回滚。
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
/**
获取当前事务的状态
*/
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
/**
基于当前事务状态提交事务
*/
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
/**
基于当前事务状态回滚事务
*/
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
由于Sping boot服务中基本都会用到数据库,所以DataSourceTransactionManager便成为了最通用的基于数据源的事务管理器,也就是基于DataSource进行事务管理。而DataSource正是Java中数据源的抽象,底层可以兼容各种数据库。
3.2 数据库操作涉及的事务流程
声明式事务是依赖于AOP实现的,所以这部分内容可以参考«【Spring基础】AOP»。userService.selectByPrimaryKey(id)实际上是实现类UserServiceImpl去调用selectByPrimaryKey(id)此时因为@Transactional这个注解的存在,而触发相关的切面逻辑。
3.2.1 切面逻辑触发
selectByPrimaryKey(id)调用触发对应的Advice也就是TransactionInterceptor中的对应的invoke方法执行。
3.2.2 invokeWithinTransaction调用
invokeWithinTransaction贯穿整个事务的声明周期,这也就是声明式事务作用的核心方法。基于Spring可扩展性的设计,里面肯定是一系列模板方法,可以由子类去扩展。 下面就是执行selectByPrimaryKey(id)过程中与事务相关的日志,核心流程如下:
DataSourceTransactionManager [http-nio-9314-exec-3] :370 Creating new transaction with name [xxxMethod]: PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ISOLATION_DEFAULT
DataSourceTransactionManager [http-nio-9314-exec-3] :265 Acquired Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@57abfce5] for JDBC transaction
DataSourceTransactionManager [http-nio-9314-exec-3] :283 Switching JDBC Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@57abfce5] to manual commit
// mapper sql
DataSourceTransactionManager [http-nio-9314-exec-3] :741 Initiating transaction commit
// 底层JDBC事务提交
DataSourceTransactionManager [http-nio-9314-exec-3] :328 Committing JDBC transaction on Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@57abfce5]
// 释放JDBC连接,归还给连接池
DataSourceTransactionManager [http-nio-9314-exec-3] :387 Releasing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@57abfce5] after transaction
- 选择事务管理器 – determineTransactionManager
- 创建事务 – createTransactionIfNecessary
- 业务方法调用 – invocation.proceedWithInvocation()
- 如果有异常抛出进行回滚 – completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex)
- 成功执行,提交事务 – commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
3.3 事务的创建
本文开头列举出了Spring事务中的传播属性。那这些属性是如何影响事务的运行和提交,比如说REQUIRES_NEW是如何中断当前已经存在的事务,又是如何恢复的?
3.3.1 资源绑定
Spring中事务初始化过程中,一个很重要的过程就是要将相关资源与当前线程绑定(ThreadLocal)。比如说TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource会将
数据库连接和当前线程绑定,以下日志可以看出来。
[2022-01-22T20:22:57] TRACE o.s.t.s.TransactionSynchronizationManager [http-nio-8083-exec-2] :196 Bound value [org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.ConnectionHolder@7650106] for key [{
CreateTime:"2022-01-22 20:22:13",
ActiveCount:1,
PoolingCount:0,
CreateCount:1,
DestroyCount:0,
CloseCount:3,
ConnectCount:4,
Connections:[
]
}] to thread [http-nio-8083-exec-2]
3.3.2 中断事务(suspend)
首先,出现中断事务,一般是在事务嵌套中,比如说serviceA内部某个方法调用了serviceB内部的某个方法。我们在前面提到,Spring中的事务和当前线程绑定,所以中断事务实现流程大致为:
- 维护当前事务的状态,封装到一个结构中
SuspendedResourcesHolder - 将当前线程绑定的事务资源切换为成为新事务资源
- 执行新事务逻辑,完成后提交
- 在后置清理阶段,如果当前事务有相关的
SuspendedResourcesHolder, 则与当前线程再次绑定,继续完成剩余逻辑
| 时间 | 操作 |
|---|---|
| T1 | 当前线程绑定事务A相关资源 |
| T2 | 事务A执行 |
| T3 | 事务B执行,解除当前线程与事务A的绑定,存储相关的资源到SuspendedResourcesHolder。 重新绑定与事务B的相关资源 |
| T4 | 事务B执行,收尾工作中检测到有父事务的资源,则重新和当前线程绑定 |
| T5 | 事务A继续执行 |
3.4 事务的超时机制 – Transactional timeout
3.4.1 工作原理
3.4.2 方法执行超时 - 触发TransactionTimedOutException
如下面的案例,事务设置了超时时间,等到执行的SQL的时候,已经超过设定的timeout,所以抛出TransactionTimedOutException。这个检查点 是在正式执行SQL之前(prepareStatement)。
@Override
@Transactional(timeout = 3)
public User selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return super.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
org.springframework.transaction.TransactionTimedOutException: Transaction timed out: deadline was Thu Jan 20 17:17:40 CST 2022
at org.springframework.transaction.support.ResourceHolderSupport.checkTransactionTimeout(ResourceHolderSupport.java:155)
at org.springframework.transaction.support.ResourceHolderSupport.getTimeToLiveInMillis(ResourceHolderSupport.java:144)
at org.springframework.transaction.support.ResourceHolderSupport.getTimeToLiveInSeconds(ResourceHolderSupport.java:128)
at org.mybatis.spring.transaction.SpringManagedTransaction.getTimeout(SpringManagedTransaction.java:137)
at org.apache.ibatis.executor.SimpleExecutor.prepareStatement(SimpleExecutor.java:85)
at org.apache.ibatis.executor.SimpleExecutor.doQuery(SimpleExecutor.java:62)
at org.apache.ibatis.executor.BaseExecutor.queryFromDatabase(BaseExecutor.java:325)
at org.apache.ibatis.executor.BaseExecutor.query(BaseExecutor.java:156)
at org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor.query(CachingExecutor.java:109)
at org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor.query(CachingExecutor.java:83)
at org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession.selectList(DefaultSqlSession.java:148)
at org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession.selectList(DefaultSqlSession.java:141)
at org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession.selectOne(DefaultSqlSession.java:77)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate$SqlSessionInterceptor.invoke(SqlSessionTemplate.java:433)
at com.sun.proxy.$Proxy88.selectOne(Unknown Source)
at org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate.selectOne(SqlSessionTemplate.java:166)
at org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod.execute(MapperMethod.java:75)
at org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy.invoke(MapperProxy.java:53)
at com.sun.proxy.$Proxy89.selectByPrimaryKey(Unknown Source)
at com.jacoffee.usercenter.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.selectByPrimaryKey(UserServiceImpl.java:46)
at com.jacoffee.usercenter.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.selectByPrimaryKey(UserServiceImpl.java:20)
at com.jacoffee.usercenter.service.impl.UserServiceImpl$$FastClassBySpringCGLIB$$b0339445.invoke(<generated>)
at org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy.invoke(MethodProxy.java:218)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$CglibMethodInvocation.invokeJoinpoint(CglibAopProxy.java:771)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:163)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$CglibMethodInvocation.proceed(CglibAopProxy.java:749)
3.4.3 SQL执行超时 - 触发MySQLTimeoutException
@Override
@Transactional(timeout = 3)
public User selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id) {
// selectByPrimaryKey --> mapper中配置的 select sleep(5);
return super.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
Cause: com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.MySQLTimeoutException: Statement cancelled due to timeout or client request### The error may exist in file [/Users/allen/Study/Projects/user-center/target/classes/com/jacoffee/usercenter/mapper/UserMapper.xml]### The error may involve com.jacoffee.usercenter.mapper.UserMapper.selectByPrimaryKey-Inline### The error occurred while setting parameters### SQL: select sleep(5)### Cause: com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.MySQLTimeoutException: Statement cancelled due to timeout or client request; Statement cancelled due to timeout or client request; nested exception is com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.MySQLTimeoutException: Statement cancelled due to timeout or client request] with root cause
com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.MySQLTimeoutException: Statement cancelled due to timeout or client request
at com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement.executeInternal(PreparedStatement.java:1923)
at com.mysql.jdbc.PreparedStatement.execute(PreparedStatement.java:1242)
at com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidPooledPreparedStatement.execute(DruidPooledPreparedStatement.java:497)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdbc.PreparedStatementLogger.invoke(PreparedStatementLogger.java:59)
内部维护一个超时检查任务,去检查超时。下面的代码可以看出executeInternal执行的时候,内部提交了一个timeoutTask,因此在SQL执行超时才会出现上面的调用栈。
检查逻辑: 指定时间去触发某个任务,然后cancel相应的statement, 也就是直接kill掉 KILL QUERY trxId
// com.mysql.jdbc.StatementImpl
public class StatementImpl implements Statement {
/**
* Thread used to implement query timeouts...Eventually we could be more
* efficient and have one thread with timers, but this is a straightforward
* and simple way to implement a feature that isn't used all that often.
*/
class CancelTask extends TimerTask {
}
private boolean executeInternal(String sql, boolean returnGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {
if (locallyScopedConn.getEnableQueryTimeouts() && this.timeoutInMillis != 0 && locallyScopedConn.versionMeetsMinimum(5, 0, 0)) {
timeoutTask = new CancelTask(this);
locallyScopedConn.getCancelTimer().schedule(timeoutTask, this.timeoutInMillis);
}
}
}
3.5 事务同步机制 – TransactionSynchronization
嵌入事务生命周期各个阶段的回调,比如说:
- 事务提交之前的关联操作
beforeCommit() - 事务提交之后的关联操作
afterCommit()
3.5.1 典型应用
- 在某个事务提交之后,进行某些操作。比如说用户注册之后,发送相关的邮件; 如下例通过TransactionSynchronizationManager注册发送消息的同步操作
@Override
public int insert(User model) {
int affected = super.insert(model);
// ! 在当前事务中 注册同步处理器, 事务提交之后,向消息队列发送消息
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new TransactionSynchronization() {
@Override
public void afterCommit() {
TransactionSynchronization.super.afterCommit();
// kafkaProducer.send
}
});
return affected;
}
3.5.2 同步逻辑注册
通过TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization注册当前事务对应的 同步逻辑,由于事务和线程绑定,所以正好可以利用ThreadLocal维护线程对应的 Synchronizations。
public abstract class TransactionSynchronizationManager {
/**
* ! 因为事务和 线程绑定, 所以同步操作正好可以利用ThreadLocal
* ! 一个事务 可以注册多个 同步逻辑
*/
private static final ThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>> synchronizations = new NamedThreadLocal<>("Transaction synchronizations");
public static void registerSynchronization(TransactionSynchronization synchronization) {
synchronizations.get().add(synchronization);
}
}
3.5.3 触发时机
事务管理器内部进行事务提交之后,会触发相应的回调 – triggerAfterCommit
// AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
// ! 事务管理器在提交之后, 暴露的回调,其中事务同步机制就是在该逻辑中出来的
// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
try {
triggerAfterCommit(status);
}
}
3.5.4 清除时机
整个事务操作完成之后,会有一个收尾工作,如果注册了同步进制也会进行清除。上面我们提到过,底层的同步机制是使用ThreadLocal维护的,该结构经常会考察的点就是内存泄露, 所以clear()方法底层肯定是清除线程对应的数据结构。
// AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
/**
* Clean up after completion, clearing synchronization if necessary,
*
* and invoking doCleanupAfterCompletion.
*
* @param status object representing the transaction
* @see #doCleanupAfterCompletion
*/
private void cleanupAfterCompletion(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.clear();
}
}
// TransactionSynchronizationManager
/**
* ! 清除当前线程的 相关的事务同步结构
* Clear the entire transaction synchronization state for the current thread:
* registered synchronizations as well as the various transaction characteristics.
*
*/
public static void clear() {
synchronizations.remove();
...
}
4. @Transactional注解失效场景
一般最好是放在需要事务支持的方法上(method over class),因为一个类中的其它方法,可能根本不需要事务,就比如说只读相关方法。
The Spring team recommends that you annotate only concrete classes (and methods of concrete classes) with the @Transactional annotation, as opposed to annotating interfaces.
Spring官方团队建议该注解最好只是用在实体类 或者 实体类的方法上面。
4.1 没有被Spring管理的类
一般我们会使用@Transactional注解Service的实现类,另外基于@Transactional实现原理,Spring在加载Bean的时候,根据@Transantional生成相应的Advice,如果没有添加组件类注解(@Transactional,@Component),都不会被加载,自然也不能生成对应的Advice。
// @Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
public void insert() {}
}
4.2 @Tranactional只能对于被public方法生效
因为基于Cglib生成代理的时候,AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource方法寻找方法注解的时候,默认只会寻找public方法。
class AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource {
public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource() {
this(true);
}
/**
Create a custom AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource, supporting
public methods that carry the {@code Transactional} annotation
or the EJB3 {@link javax.ejb.TransactionAttribute} annotation.
*/
public AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(boolean publicMethodsOnly) {
}
}
4.3 AOP限制 – 不能自身调用(proxy based)
只有主调为代理而不是this,才会触发相应的切面逻辑
// @Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
public void insert() {}
}
4.4 异步没有抛出或者抛出的异常不支持回滚
- 异常没有抛出直接try catch吞掉了,相当于rollback不起作用
@Transactional(rollbackFor = {Exception.class})
public void insert(User user) {
try {
} catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
- 需要回滚的异常和抛出来的异常不一样
@Transactional(rollbackFor = {BusinessException.class})
public void insert(User user) {
// 实际抛出 -- SQLException
// throw new SQLException
}
5. 参考
> 官网 事务管理