1. 定义
面向切面的核心是切面,正如面向对象的核心是对象一样。它提供了一种机制可以让我们在切面,可以狭义的理解为在方法的执行点前后添加各种处理逻辑,以最小侵入式的方式
来添加或者扩展额外的逻辑,减少其与业务逻辑代码的耦合,典型的运用如声明式事务编程、方法执行时间的统计、方法重试、权限验证(AuthorizationInterceptor)
另外要明确的一点就是Spring AOP是基于代理的(It is important to grasp the fact that Spring AOP is proxy-based)。
In the Spring Framework, an AOP proxy will be a JDK dynamic proxy or a CGLIB proxy(在Spring框架中,AOP代理要么是动态代理要么是CGLIB代理,后者是基于态字节码生成实现,前者是基于JDK动态代理实现的)
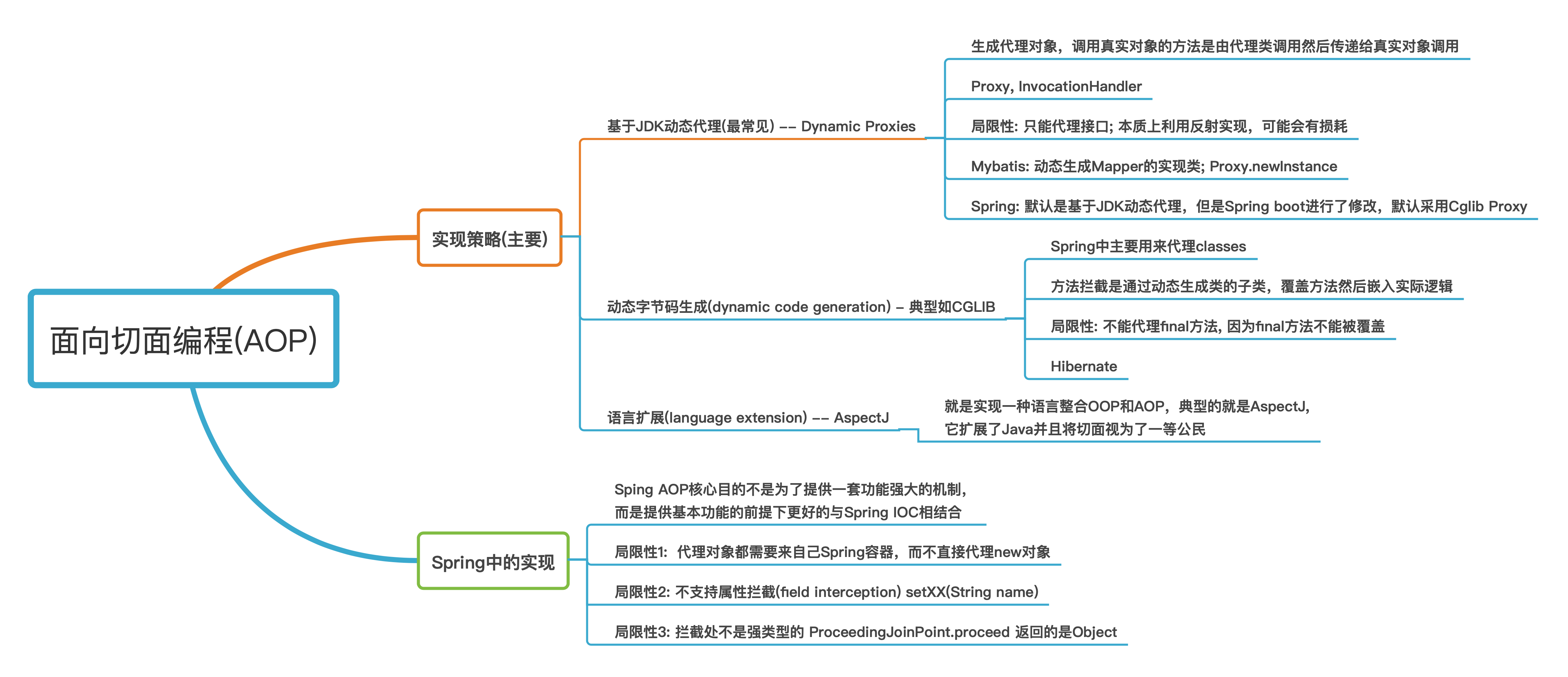
1.1 基本术语
-
Join point: 在Spring中可以理解为方法执行点 -
Advice: 切面要做的事情(重试,记录调用时长)。根据类型可分为(around,beofre,after)等,在Spring中的Advice主要是拦截器
public interface Interceptor extends Advice {
}
-
Pointcut: 切入点,实际上就是如何锁定要添加的Advice的地址,带Retry的method、所有Controller的方法等。 Spring AOP默认使用AspectJ pointcut表达式(matching the execution of methods on Spring beans) -
Target object: 需要增强的对象(object being advised),由于Spring AOP使用的是运行时代理,所以Target对象肯定是代理对象(Since Spring AOP is implemented using runtime proxies, this object will always be aproxiedobject) -
Advisor = Pointcut + Advice: 如AspectJPointcutAdvisor就融合了AbstractAspectJAdvice 和 PointcutAdvisor -
Weaving: 将切面逻辑整合进入目标对象形成最终对象的过程(Advised object)
The process of linking aspects with the targeted object to create the advised object
public interface Advised {
/**
* 被代理的"源"信息
* Return the {@code TargetSource} used by this {@code Advised} object.
*/
TargetSource getTargetSource();
}
在实际编码中,我们可以基于此拿到某个【代理对象】的被代理类的相关信息
((Advised) proxy).getTargetSource()
从源码上来看,Advised接口的实现类都是AdvisedSupport、AspectJProxyFactory;这些看起来就像工厂类,但并不是实际工厂类
1.2 织入类型(weaving type)
前三种需要结合AspectJ的具体使用才能更好的理解
| 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 编译期织入(Compile-time weaving) | 在代码编译期间完成织入 |
| 后编译期织入(Post-compile weaving) | 编译后完成织入 |
| 加载时织入(Load-time weaving) | Class加载的时候完成织入 |
| 运行时织入(runtime weaving) -- Spring AOP | 运行的时候完成织入 |
1.3 Spring Aop vs AspectJ
| Spring AOP | AspectJ |
|---|---|
| 纯Java | |
| 只能运行时织入 | 支持编译期织入、后编译期织入、加载时织入 |
| 只支持方法级别的织入 | 支持属性、方法、构造器等织入 |
| 只能在Spring Bean上实现 | 所有的领域对象都能实现 |
| Supports only method execution pointcuts | Support all pointcuts |
| 在目标对象上创建代理,然后再代理上施加切面逻辑 | Aspects are weaved directly into code before application is executed (before runtime) |
| 不支持self-invocation代理 | 支持self-invocation代理 |
2. 基本使用
2.1 声明式事务 – 最核心的应用
实际使用参见【Spring基础】事务中的声明式事务部分
2.2 方法执行时间统计
2.3 方法调用重试
3. 动态代理实现 – 显然不可能是静态代理
If the target object to be proxied implements at least one interface then a JDK dynamic proxy will be used.
All of the interfaces implemented by the target type will be proxied. If the target object does not implement any interfaces then a CGLIB proxy will be created.
3.1 JDK动态代理(JDK Dynamic Proxy)
Spring AOP defaults to using standard JDK
dynamic proxiesfor AOP proxies. This enables any interface (or set of interfaces) to be proxied.
这是Spring中默认的AOP实现, 也就是用作接口代理的(被代理类型必须实现某个接口)。 JDK动态代理实现参考 【反射】动态代理。
3.2 CGLIB的动态代理(Dynamic Byte Code Generation)
Spring AOP can also use CGLIB proxies. This is necessary to proxy classes rather than interfaces. CGLIB is used by default if a business object does not implement an interface
如果业务对象没有继承接口,Spring AOP默认会使用CGLIB代理,它是基于字节码增强的技术实现的。
To add the ability to proxy against classes, we need to go beyond the capabilities of dynamic proxies and move to dynamic byte code generation
为了增强对于类的代理功能,仅仅是动态代理还不够(JDK的动态代理是基于接口的),还需要动态的字节码生成。
3.3 JDK Dynamic Proxy vs CGLIB Proxy
| 比较纬度 | JDK Dynamic Proxy | CGLIB Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| 代理对象 | 只能代理实现了接口的对象 | 普通的对象也行 |
| 拦截机制 | 在Proxy上的方法调用会传递给与Proxy对象关联的InvocationHandler | 在Proxy方法调用会传递给AbstractAspectJAdvice的invoke方法 |
4. 底层实现之代理生成 - AbstractAutoProxyCreator
{@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor} implementation that wraps each eligible bean with an AOP proxy, delegating to specified interceptors before invoking the bean itself.
总结一句话就是:
BeanPostProcessor前置处理器(
postProcessBeforeInitialization)判断Bean是否需要生成代理并维护全局标志(由于Bean可能被同时处理,所以使用ConcurrentHashMap),同时基于@Aspect类中的方法,形成一系列Advice。后置处理器(
postProcessAfterInitialization)根据前置处理器维护的标识为需要生成代理的Bean,基于Advisor创建ObjenesisCglibAopProxy代理。
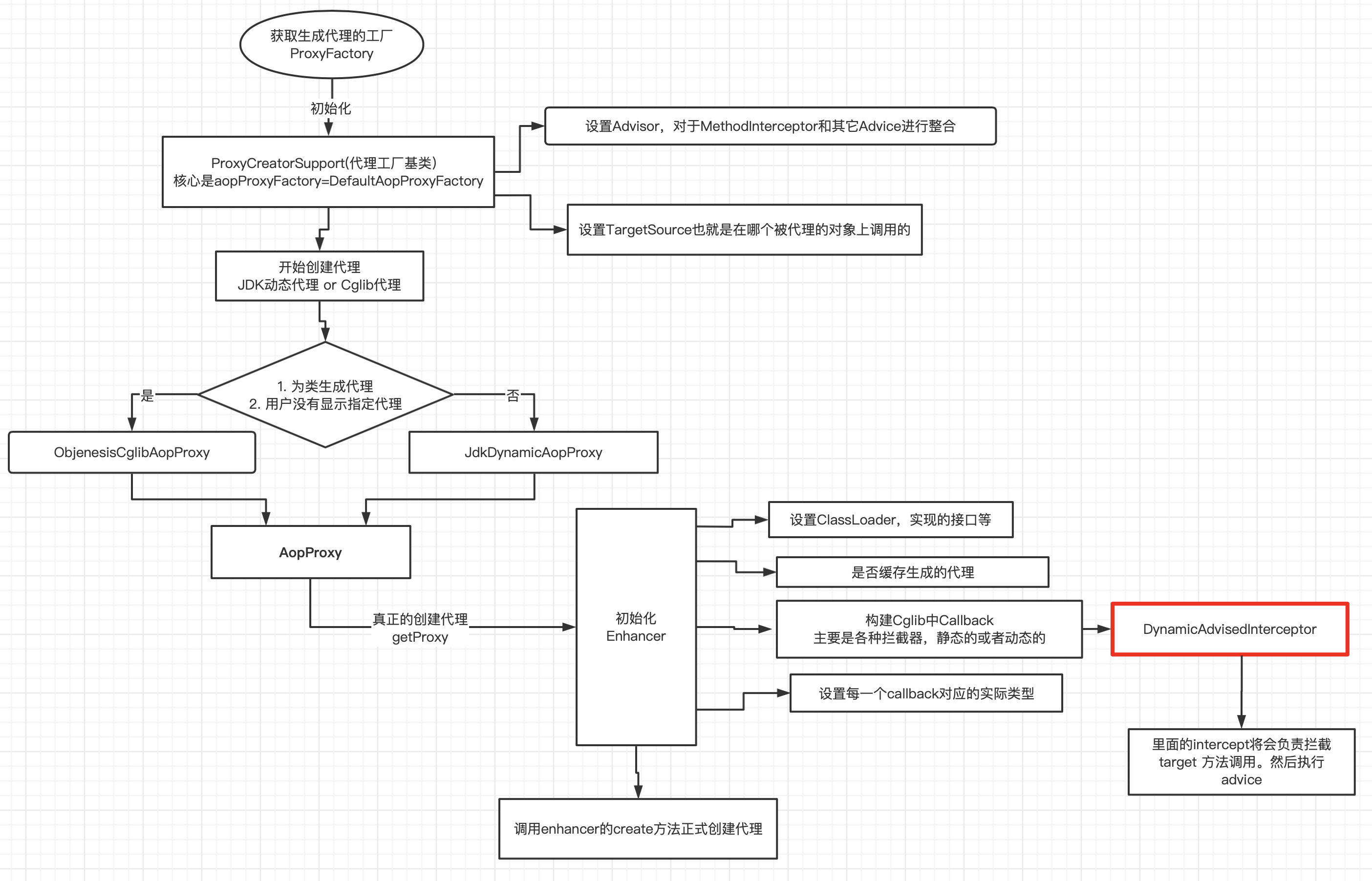
大致执行流程图:
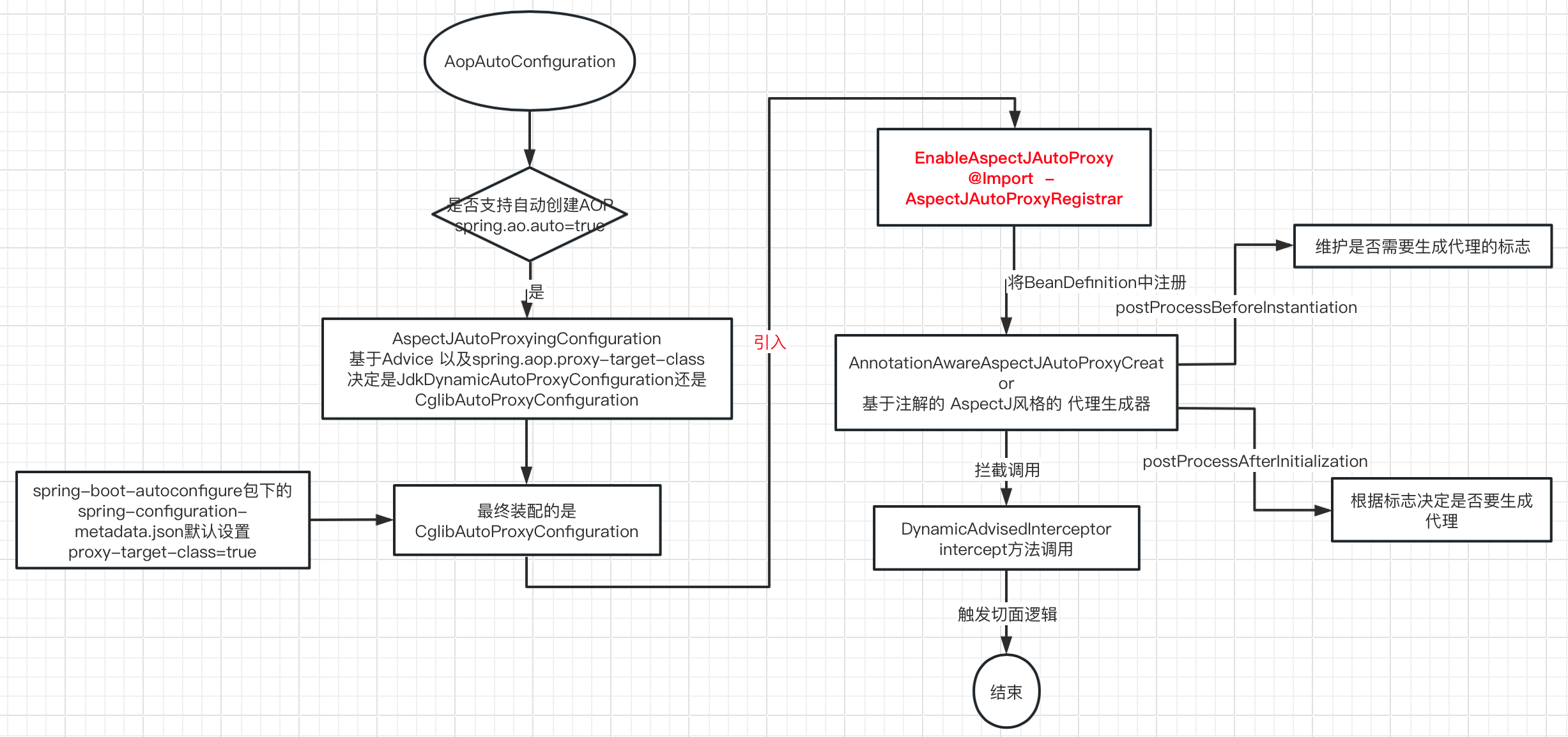
下面以拦截被@JedisLockDesc注解(支持为方法增加基于Jedis分布式锁实现)修饰的方法为例,说明基于AspectJ AOP的生成和调用流程。
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class JedisLockAnnotationProcessor {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.jacoffee.contentcenter.configuration.JedisLockDesc)")
public void pointCut() {
}
@Around(value = "pointCut()")
public Object intercept(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature();
JedisLockDesc jedisLockDesc = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(JedisLockDesc.class);
int acquireTimeoutMillis = jedisLockDesc.acquireTimeoutMillis();
System.out.println("method invocated");
return pjp.proceed();
}
}
@Component
public class NodeScheduler {
@Autowired
private ShareController shareController;
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000L)
// @JedisLockDesc(lockPath = "xx", acquireTimeoutMillisString = "${node.lock.timeout}")
// @JedisLockDesc(lockPath = "xx", acquireTimeoutMillisString = "#{nodeConfig.acquireTimeout}")
@JedisLockDesc(lockPath = "xx", acquireTimeoutMillisString = "5000")
public Long testScheduled() {
shareController.reallyRun();
return 1L;
}
}
Spring中的AOP默认实现工厂类org.springframework.aop.framework.DefaultAopProxyFactory, 其中的createAopProxy方法明确定义了什么时候使用JDK动态代
理,什么时候使用 CGLIB代理,它们之间一个明显的区别就是是否允许代理类。
4.1 Autoconfigure配置文件默认设置spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true。
Spring-boot-autoconfigure包下spring-configuration-metadata.json文件默认会设置一系列属性,比如说将是否代理class默认设置成了true
public class MetadataStore {
static final String METADATA_PATH = "META-INF/spring-configuration-metadata.json";
private static final String ADDITIONAL_METADATA_PATH = "META-INF/additional-spring-configuration-metadata.json";
// 初始化的时候会调用该方法进行配置解析
public ConfigurationMetadata readMetadata() {
....
}
}
{
"name": "spring.aop.auto",
"type": "java.lang.Boolean",
"description": "Add @EnableAspectJAutoProxy.",
"defaultValue": true
},
{
"name": "spring.aop.proxy-target-class",
"type": "java.lang.Boolean",
"description": "Whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created (true), as opposed to standard Java interface-based proxies (false).",
"defaultValue": true
}
4.2 AopAutoConfiguration基于Advice类自动装配了CglibAutoProxyConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration中默认会生成CglibAutoProxyConfiguration,与此同时EnableAspectJAutoProxy中的是否为类生成代理类设置成为true。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public class AopAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
}
4.3 EnableAspectJAutoProxy引入注册用于生成代理的Creator, 如AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
EnableAspectJAutoProxy = Enable + AspectJ + AutoProxy === 自动生成AspectJ风格的AOP — @AspectJ-based AOP
Enables support for handling components
marked with AspectJ's {@code @Aspect} annotation
Note that {@code @Aspect} beans may be component-scanned like any other. Simply mark the aspect with both {@code @Aspect} and {@code @Component}
从 EnableAspectJAutoProxy 源码中我们可以看出,它引入了AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar,主要用于处理带@Aspect的组件,既然是组件所以需要是Component(Service, Component)以便能够被扫描。
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)
public class @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
}
// 扫描@Aspect
public class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar {
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry
) {
...
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {
// 该方法调用完之后,会将AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的proxyTargetClass属性设置为true
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
...
}
}
因此Spring注册了用于创建代理的Creator的BeanDefintion, 内置的是InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator、AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator, AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这三个,最终根据优先级注册是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator也就是支持基于注解生成代理的,
beanName为internalAutoProxyCreator。
public abstract class AopConfigUtils {
/**
* The bean name of the internally managed auto-proxy creator.
*/
public static final String AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME =
"org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator";
static {
// Set up the escalation list...
APC_PRIORITY_LIST.add(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class);
APC_PRIORITY_LIST.add(AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class);
APC_PRIORITY_LIST.add(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
}
@Nullable
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(
Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
}
}
4.4 Bean初始化阶段AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator开始生成Bean对应Advice以及维护bean是否需要生成代理的标志位
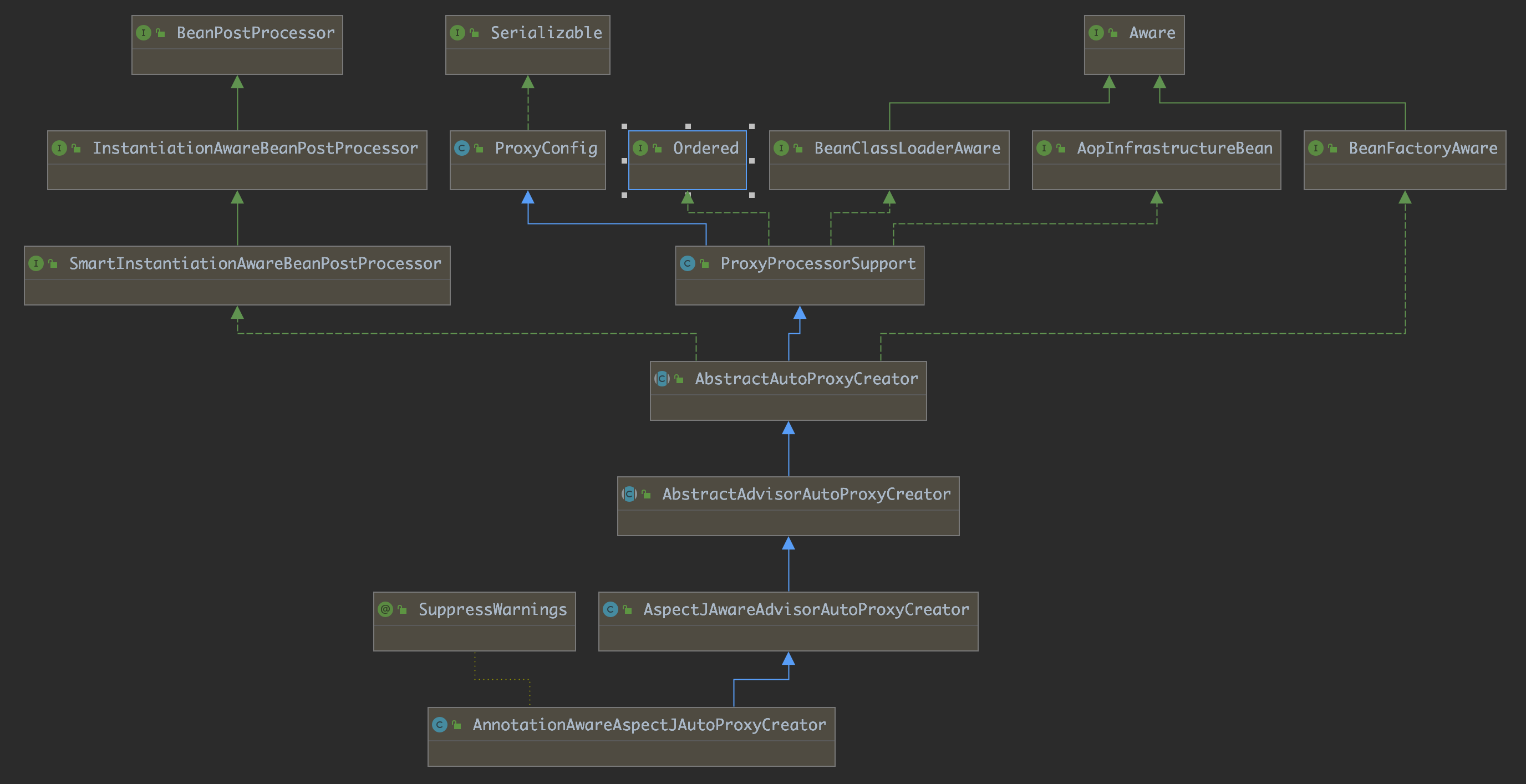
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator = AnnotationAware + AspectJ + AutoProxyCreator <: BeanPostProcessor
{@link AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator} subclass that
processes all AspectJ annotation aspects in the current application context, as well as Spring Advisors.Any AspectJ annotated classes will automatically be recognized, and their
advice applied if Spring AOP's proxy-based model is capable of applying it. This covers method execution joinpoints.
从源码注释我们可以看到AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator主要负责所有被@Aspect标记的注解类。
从它的UML图中我们看出它是BeanPostProcessor的子类,那么自然而然的会去关注两个声明周期方法的逻辑。
4.4.1 postProcessBeforeInstantiation
主要用于判断某个Bean是否需要生成对应的AdvisedBean, 相当于提前生成一个标记位。 像上面提到的JedisLockAnnotationProcessor由于被@Aspect注解修饰所以不会再被Advised,所以advisedBeans中的值为false。
/**
* 是否需要生成代理的标志位
*/
private final Map<Object, Boolean> advisedBeans = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/**
Subclasses should override this method to return {@code true} if the
given bean should not be considered for auto-proxying by this post-processor.
*/
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
return false;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
这个地方的核心逻辑就是要搞清楚: 不应该生成代理的条件
- 基础组件类是不用再生成代理的: Advice、Pointcut、Pointcut等, 这也就是isInfrastructureClass的逻辑。
- 被@Apspect注解的组件本来就是去对别的Bean进行处理的,所以也不需要。实际上这类就是 AspectJPointcutAdvisor
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class JedisLockAnnotationProcessor implements EmbeddedValueResolverAware {
}
4.4.2 postProcessAfterInitialization
会根据Bean在advisedBeans的标记位以及配置的Advisor来生成对应的代理
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 如果不是advisedBean 即不需要生成相应代理的 则直接返回
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
// 寻找当前bean是否在beforeInitialization阶段注册了Advice
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
// 然后正式创建代理
Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
}
AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory: 负责 PointCut、Around、Before、After等注释处理, 而实际的代理生成由ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory负责
4.4.3 具体流程
- 寻找@Aspect标注的Bean
// org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
// 判断
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
}
}
- 获取带@Aspect注解的Bean之后,开始寻找Advisor类方法也就是
JedisLockAnnotationProcessor中的intercept, 然后基于它们生成Advisor
注意每一个Advisor方法(上面的intercept)都会生成一个Advisor
// org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
@Override
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
// Advisor具体实现类 InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, 0, aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
}
-
生成Advisor大致的逻辑就是pointcut + advice,首先获取@Aspect修饰类(JedisLockAnnotationProcessor)中的Advice method(intercept)上的point cut表达式,然后InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl初始化的时候,会同时初始化instantiateAdvice。
基于Advice的类型 AtPointcut、AtAround、AtBefore等生成具体的Advice, 上面的代码中使用了@Around注解,所以生成
AspectJAroundAdvice
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,
Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {
this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);
}
- 然后每个@Aspect Bean,都会生成一系列Advisor,然后缓存下来,避免重复初始化
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
如ShareController生成如下两个Advisor:
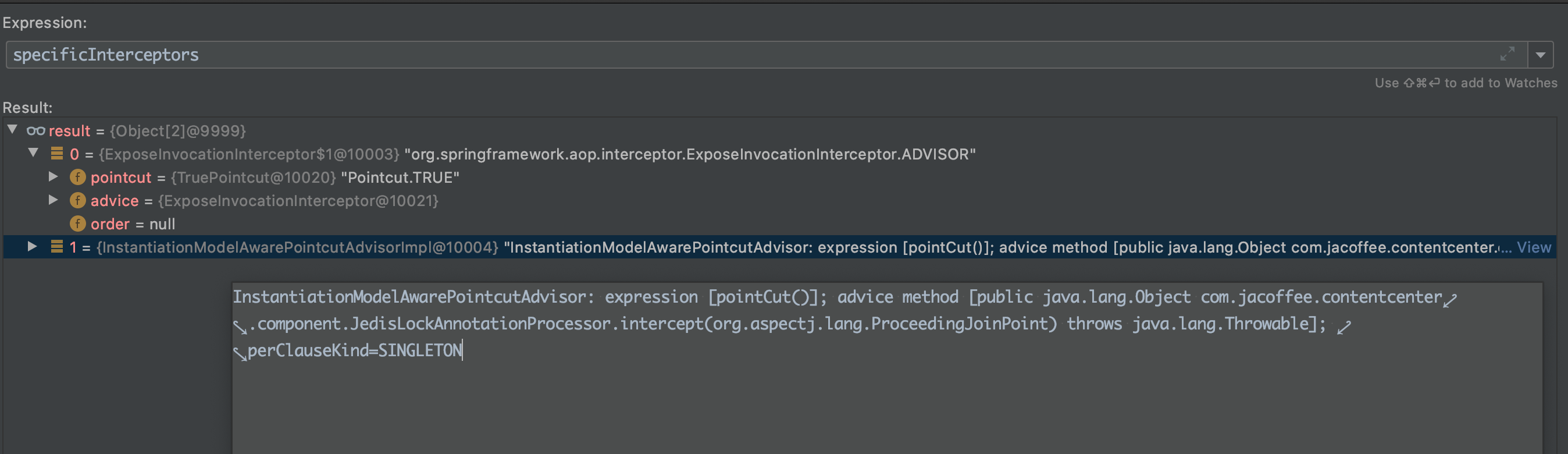
- 上述这一系列流程都是由于before initialization中的shouldSkip触发的,最终根据bean advsisor类型来决定该bean是否为需要生成代理的bean, 也就是源码中的advisedBeans中维护的标志位。 至于需要忽略就是哪些被@Aspect注解的Bean, 因为它们是不需要再被额外代理的。
// org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
// org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
@Override
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// TODO: Consider optimization by caching the list of the aspect names
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) {
if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor &&
((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) {
return true;
}
}
return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);
}
4.5 AbstractAutoProxyCreator的后置处理器开始生成Bean代理(如有需要)
AbstractAutoProxyCreator的后置处理器postProcessAfterInitialization 会决定是否为指定bean生成代理, 主要就是根据前置处理器postProcessBeforeInstantiation维护的标志位。
// org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
....
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
....
}
4.5.1 获取bean对应的Advisors
这个在前置处理器阶段已经生成并且缓存在BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder中
4.5.2 正式创建代理
基本就是要搞清楚几个问题: 如何创建代理工厂类(在Spring的思想中,肯定不会直接进行动态创建)以及创建一个Aop代理需要哪些”原料” 。
- 获取ProxyFactory, 底层会实际上初始化的是
DefaultAopProxyFactory, 也就是我们常看到的判断是初始化JDKDynamic Proxy还是CglibAopProxy的地方 - 根据上一步获取到代理实现类CglibApoProxy正式获取代理
getProxy() - 由于CglibProxy主要是基于CGLIB Enhancer实现的,所以这一步会配置各种Enhancer需要的参数,比较重要就是如何构造各种Callback(主要是MethodInterceptor, 比如说比较核心的DynamicAdvisedInterceptor)
- 配置完成,Enhancer正式开始创建代理, 后面在Spring中会看到类似的类名
NodeScheduler$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$...
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
5. 底层实现之调用拦截 – CglibMethodInvocation
这个过程也就是我们在调用被代理的类方法时,是如何触发代理类相应的增强逻辑执行的。
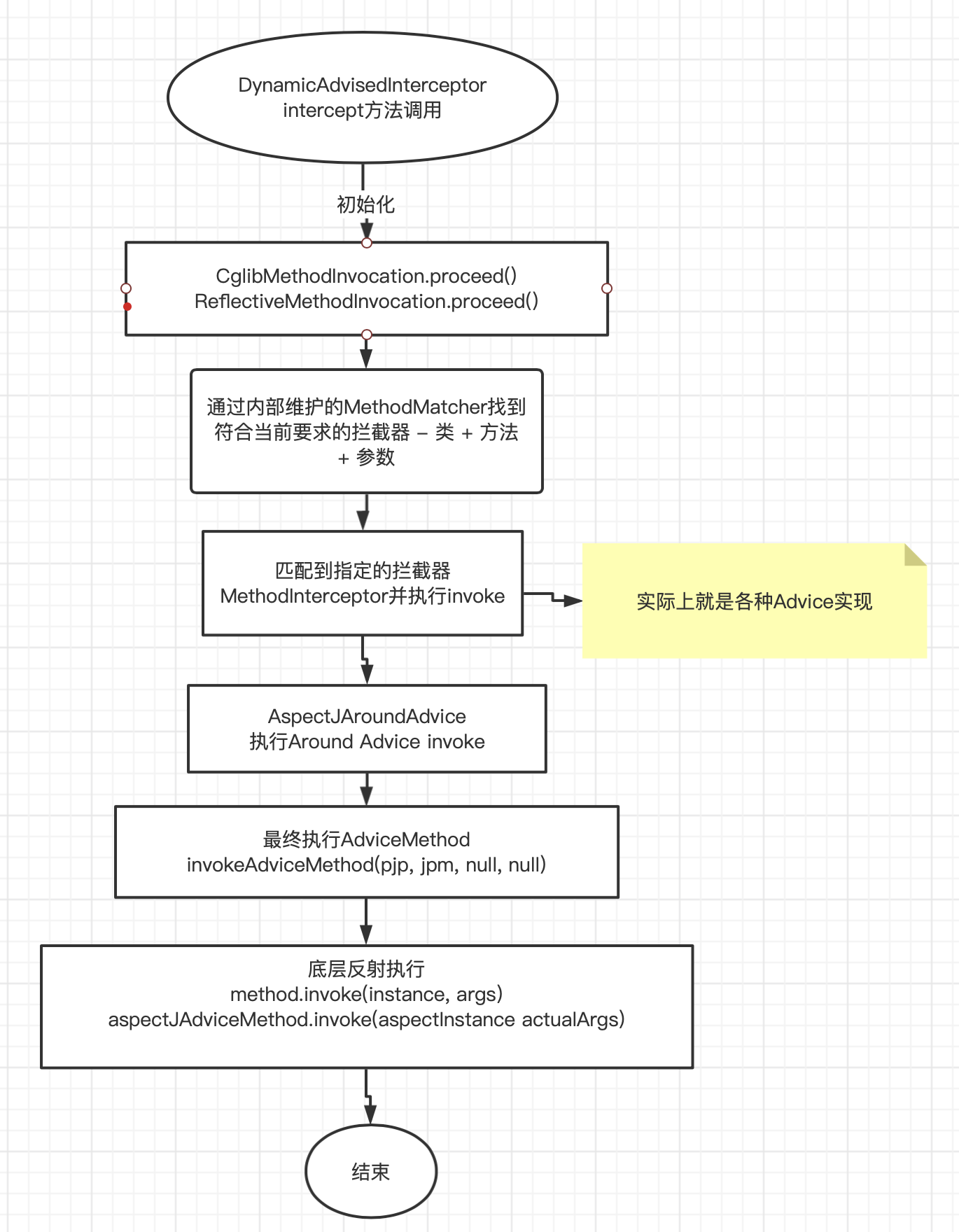
5.1 触发切面的逻辑,也就是Advice方法的调用
正如代理方法的调用会delegate给InvocationHandler的invoke方法;
AbstractAspectJAdvice(比如说AspectJAroundAdvice),在被JedisLockDesc修饰的方法调用的时候,也会触发invoke方法。
// org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJAroundAdvice
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
}
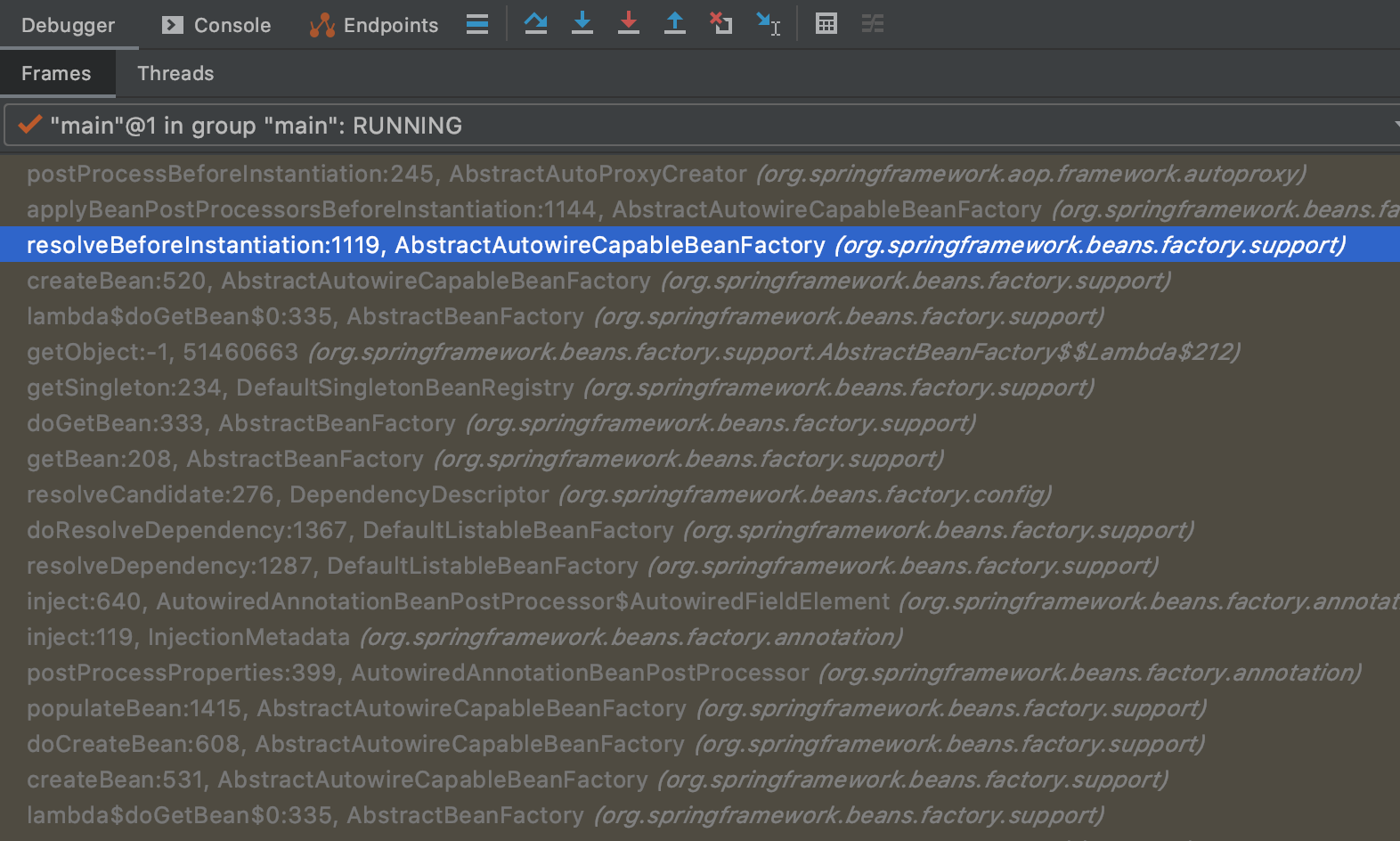
5.1.1 大致流程 ScheduledRunnable — testScheduled — CglibAopProxy$DynamicAdvisedInterceptor
大致流程参见下面的debug调用栈:
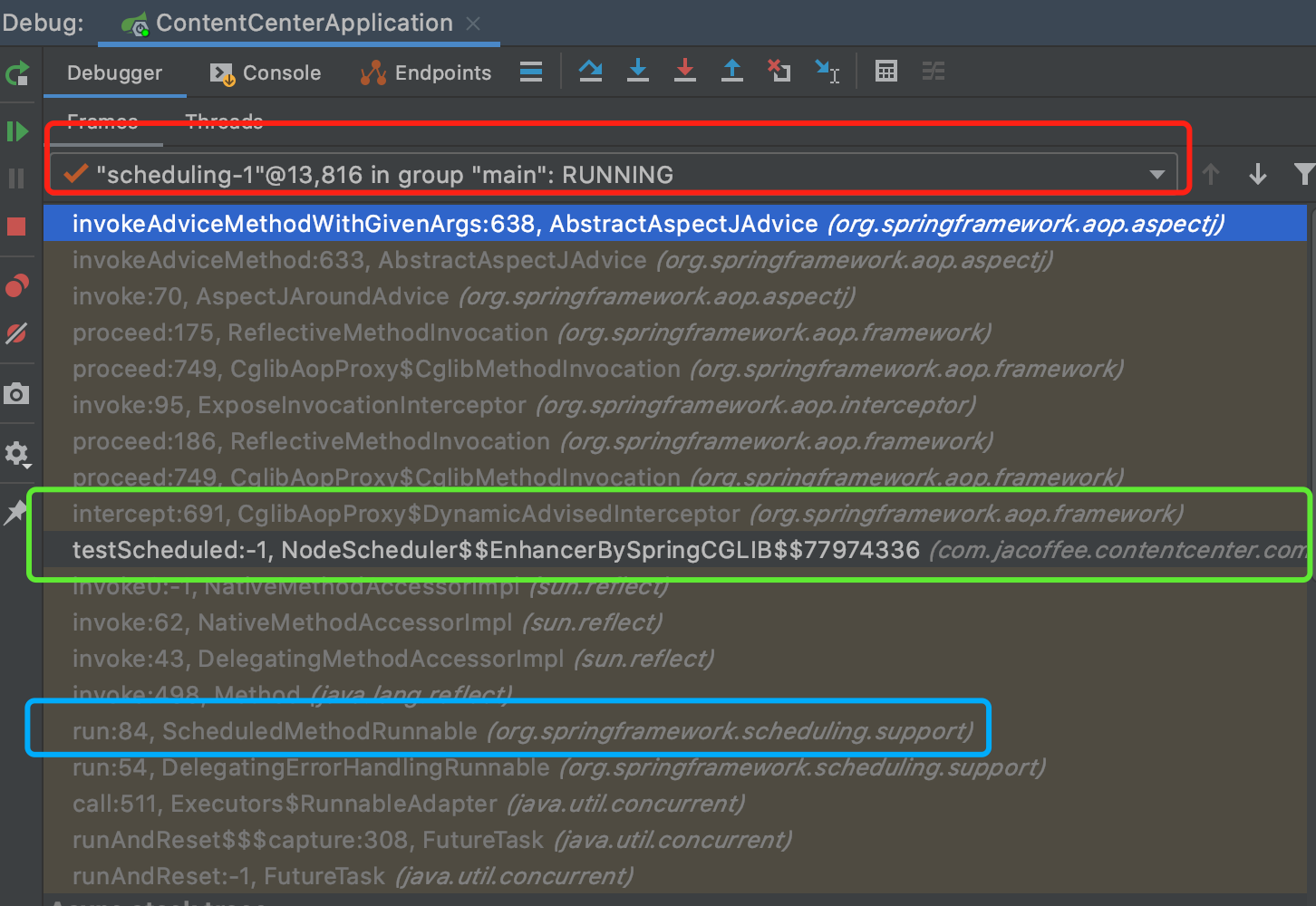
从线程名可以看出是在调度线程上运行的,间接说明调用方法是由于调度定时直接被调用,然后触发切面拦截了。同时与注解的位置是没有关系的
@JedisLockDesc(lockPath = "xx", acquireTimeoutMillisString = "5000")
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000L)
public Long testScheduled() {}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000L)
@JedisLockDesc(lockPath = "xx", acquireTimeoutMillisString = "5000")
public Long testScheduled() {}
5.1.2 关于MethodInvocation
Description of an invocation to a method, given to an interceptor upon method call. A method invocation is a joinpoint
抽象了一个方法的调用,当执行时会dispatch给拦截器。
NodeScheduler的testScheduled被定时调度执行的时候,由于此处容器中是对应的代理对象, 所以将方法调用delegate给内置的callback, 在本例中是
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor中的intercept方法。
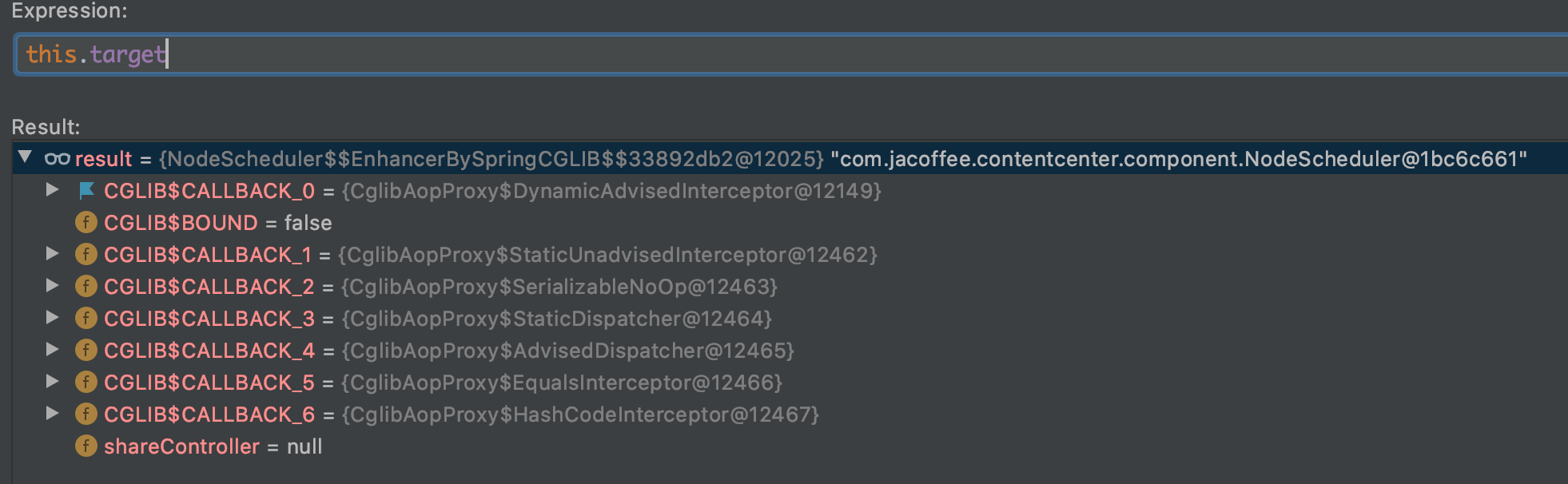
- 构建CglibMethodInvocation并且执行proceed()
- 从代理配置的拦截器中根据指定条件去执行具体拦截,比如说本例中的 AspectJAroundAdvice的invoke方法, 最终会通过反射调用 Advice method也就是上面的
testScheduled
public abstract class AbstractAspectJAdvice implements Advice, AspectJPrecedenceInformation, Serializable {
// this.aspectJAdviceMethod.toString ---> public java.lang.Object com.jacoffee.contentcenter.component.JedisLockAnnotationProcessor.intercept(org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint) throws java.lang.Throwable
// this.aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectInstance() ---> com.jacoffee.contentcenter.component.JedisLockAnnotationProcessor@cdfc980
this.aspectJAdviceMethod.invoke(this.aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectInstance(), actualArgs)
}
6. 失效场景
6.1 对同一个类方法内部的调用
@Transactional
public void A() {
B()
}
@Transactional
public void B() {}
在A方法调用B, 不会通过创建代理类访问而是直接访问
However, once the call has finally reached the target object, the SimplePojo reference in this case, any method calls that it may make on itself, such as this.bar() or this.foo(), are going to be invoked against the this reference, and not the proxy. This has important implications. It means that self-invocation is not going to result in the advice (associated with a method invocation) getting a chance to execute
public SimplePojo implements Pojo {
public void foo() {
// 若foo是通过代理调用。那么bar方法的调用,将是直接调用
this.bar()
}
public void bar() {
}
}
那么如何解决自身调用不能被代理呢?
- 逻辑重构避免再代理方法中有自身方法的调用
- 显示指定当前代理,
严重不推荐,暴露实现细节,对代码侵入性强
public SimplePojo implements Pojo {
public void foo() {
((Pojo)AopContext.currentProxy()).bar();
}
public void bar() {
}
}
另外需要注意的是: AspectJ是不会有这个问题的,因为它不是基于代理的AOP框架; 一定注意不要将AspectJ和CglibProxy搞混了。
6.2 循环依赖导致getEarlyReference被调用,结果导致代理类无法正常生成
核心原因就是为了解决循环依赖,会将Bean对象放入earlyProxyReferences中去,也就是未经过代理的。
但生成代理这一个步骤还是处理了,也就是wrapIfNecessary还是调用了
最后等到后置处理器进行的时候, 会判断对象是否在earlyProxyReferences中,如果在的话,直接跳过代理生成,因此最终还是原来的Bean。
AbstractAutoProxyCreator -- postProcessBeforeInstantiation
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator --- BeanPostProcessor
class org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator ===> postProcessBeforeInstantiation
class org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator ===> postProcessAfterInitialization
因为NodeManager和其它的bean形成了循环依赖,导致getEarlyBeanReference被调用
@Override
public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 这里存放的是代理之前的,所以肯定和下面的一样了 = this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey)
this.earlyProxyReferences.put(cacheKey, bean);
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
等到BeanPostBeanProcessor被调用的是earlyProxyReferences 中已经有nodeManager 且和传进来的一样
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
7. 参考
> 官方文档 AOP
> AOP官方文档 10.6 Proxying mechanisms
> 子路 Spring AOP底层原理课.mp4