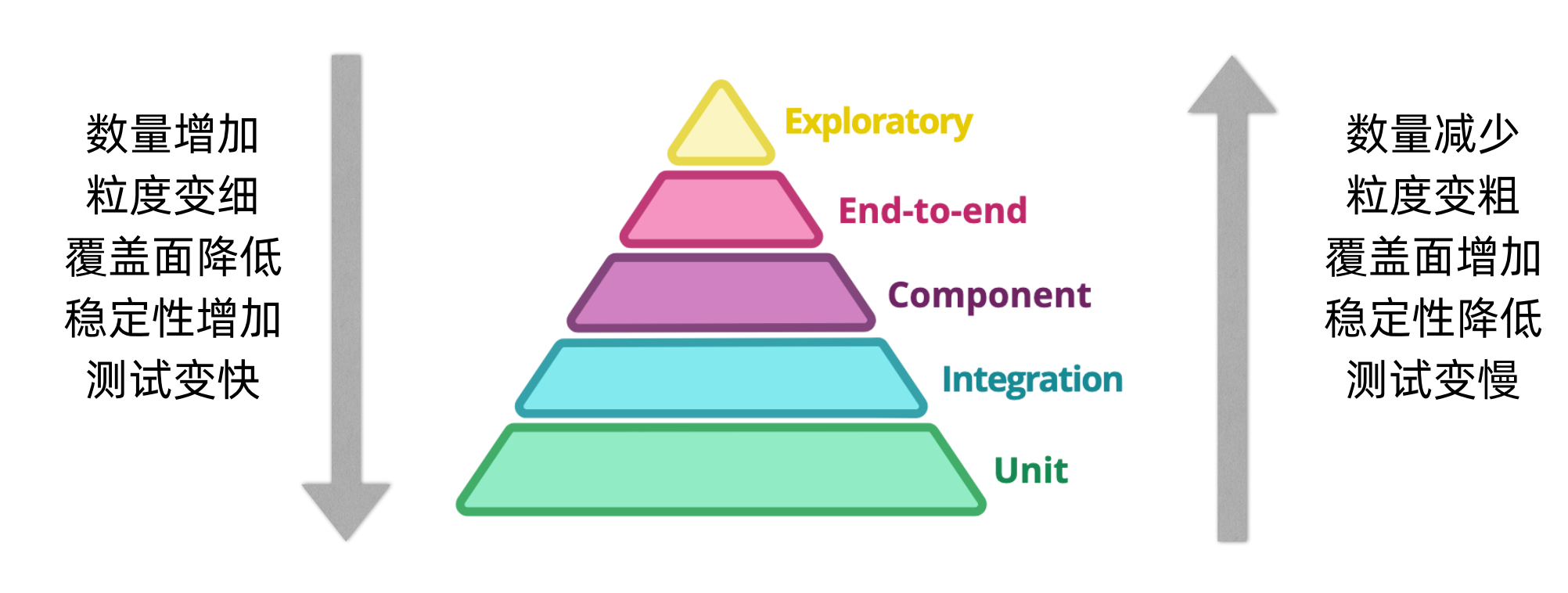
1. 测试分类
这部分梳理了常见测试的分类,有些是部分是开发参与,有的部分是测试参与,有些部分则是双方共同参与。
| 分类 | 功能 | 测试点 |
|---|---|---|
| 单元测试(Unit Test) | 确保类、模块功能正常; 只能确保单个模块正常工作 | Controller、Service、Dao等, 比如说测试Dao层,能否正常进行某种数据操作 |
| 集成测试(Integration Test) | 确保组件间交互(Controller、Service、Dao)等正常工作 – 侧重于交互 | Controller、Service、Dao之间的交互,比如说测试某个Service方法是否正常调用底层的Dao进行相关数据处理 |
| 组件测试(Component Test) | 将整个服务当前做一个黑盒 | 将分析平台当做黑盒,测试某个分析模型计算是否正常,预期的结果 |
| 端到端测试(End-to-End Test) | 将组件进一步扩展,需要多个服务之间作为整体能够正常工作 | 确保整个应用满足用户需求,比如说从flink处理实时数据,到应用层接口查询是否正常 |
2. 测试金字塔
3. 测试覆盖率
3.1 是什么
主要用于衡量测试的充分性和完整性,通常指的是代码覆盖率:至少执行一次的条目数占整个条目数的百分比。一般有如下三种代码覆盖率指标:
-
行覆盖:指的是已经被执行的语句占总可执行语句(不包括百分比、空行等)的百分比
-
判定覆盖(分支覆盖):用于度量程序中的每一个判定的分支是否都被测试到了,即某个判定,为真或为假的情况都需要测试一次
if (A > 0 & B > 0), 就要针对为真或者为假的情况,分别设计测试用例 -
条件覆盖: 这个较分支进一步细化,需要将每个条件可能的值至少满足一次。针对 if (A > 0 & B > 0)就需要分别针对 A > 0为turefalse,B > 0为ture false的情况
统计代码覆盖率的根本目的是找出潜在的遗漏测试用例,并有针对性的进行补充,同时还可以识别出代码中那些由于需求变更等原因造成的不可达的废弃代码。
3.2 如何统计 - Maven插件jacoco
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
<artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${jacoco.version}</version>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>com/**/*</include>
</includes>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>pre-test</id>
<goals>
<goal>prepare-agent</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>post-test</id>
<phase>test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>report</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<dataFile>target/jacoco.exec</dataFile>
<outputDirectory>target/jacoco-ut</outputDirectory>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
mvn test之后相关报告会写入指定的 dataFile和outputDirectory中。
3.3 jacoco报告解读
Jacoco官网有相关示例
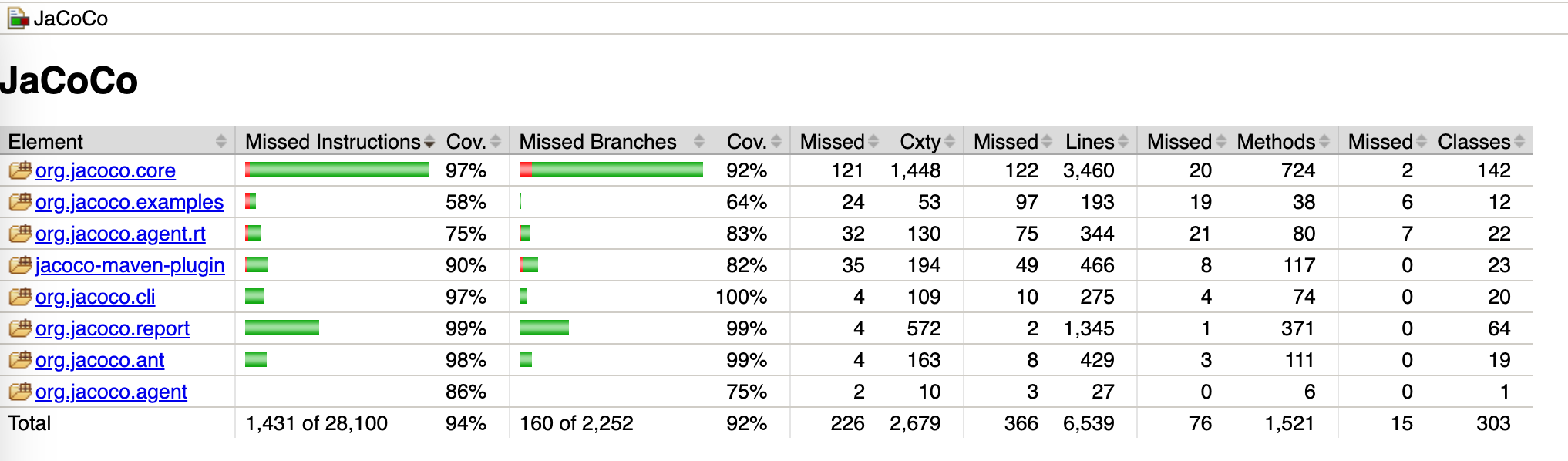
3.3.1 代码覆盖率统计报告实例
3.3.2 详细代码覆盖率实例
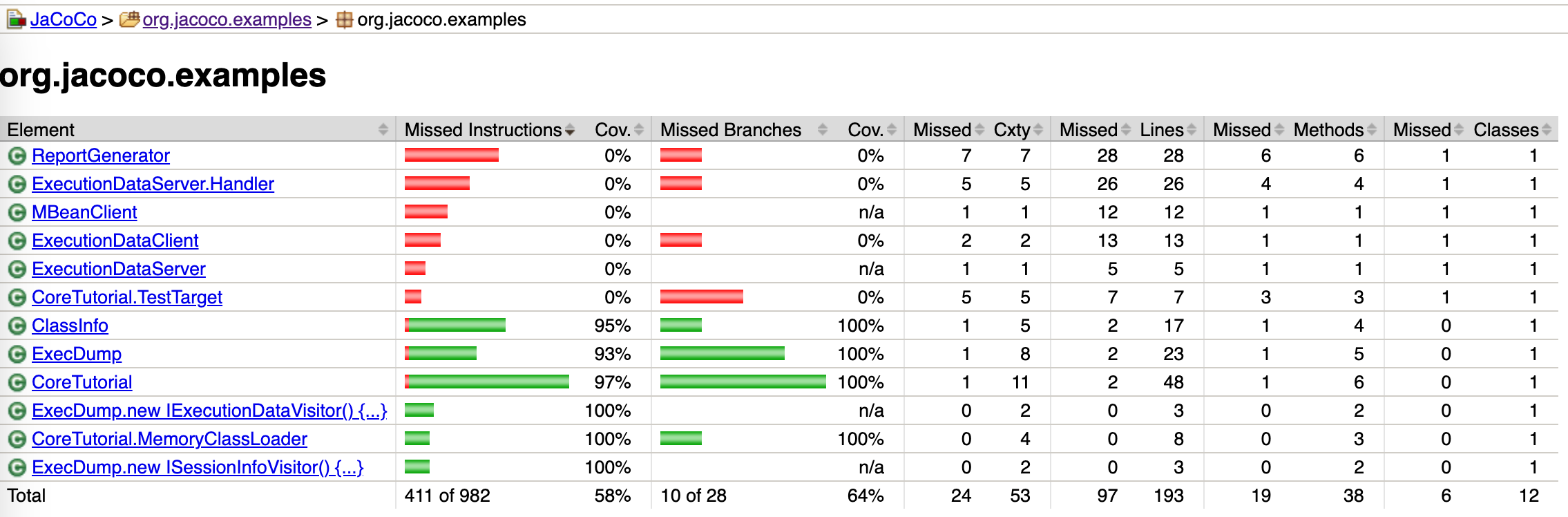
- 红色表示没有被覆盖
- 黄色表示部分被覆盖
- 绿色表示完全被覆盖
不过一般公司有集成工具的话,都会统一去做这一块,比如说在JENKINS中嵌入这一流程,然后基于此去做一些发布的卡点,覆盖率低于多少的不让发布生产之类的。
4. 重要测试工具
4.1 JUnit4 & 5
单元测试最常用的测试工具
4.2 Mockito
Mockito是一个针对Java的mocking框架,主要作用是mock请求及返回值。Mockito可以隔离类之间的相互依赖,做到真正的方法级别单测。比如说针对Service层的类进行单元测试的时候,所有的Dao层依赖都需要被mock,不需要进行实际调用,当然这个仅仅是针对单元测试而言。
5. Spring Boot测试的核心组件
在Spring Boot项目中编写测试用例的时候,我们会使用各种各样的组件(或者更准确的说注解),下面这部分主要针对常见注解以及用法进行梳理。
pom.xml依赖层面主要是 spring-boot-starter-test。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
| 注解 | 作用 | 适用测试类型 |
|---|---|---|
| @SpringBootTest | 启动整个容器,加载相关的组件 | 集成测试 – 慎用 |
| @WebMvcTest | 用于Controller层单元测试 | 单元测试 |
| @MockMvc | 提供服务器端Controller测试的相关工具 | 无 |
| @MockBean | 用来增加Mock对象,使用可以替换ApplicationContext中现有的Bean | 无 |
| @ContextConfiguration | 用于在集成测试中加载相应的ApplicationContext | 无 |
| @TestConfiguration | 在测试的时候,定制一些@Configuration以适应测试的需求 |
无 |
| @RunWith | 告知JUnit去运行该类中使用@Test注解的方法,相当于一个测试方法入口 | 无 |
| @ActiveProfiles | 加载ApplicationContext使用的环境配置,比如说@ActiveProfiles(“test”) | 无 |
5.1 @SpringBootTest – 集成测试
The @SpringBootTest annotation is useful when we need to bootstrap the entire container. The annotation works by creating the ApplicationContext that will be utilized in our tests.
We can use the webEnvironment attribute of @SpringBootTest to configure our runtime environment;
we’re using WebEnvironment.MOCK here so that the container will operate in a mock servlet environment.
@SpringBootTest is for integration tests and therefore the application.properties will be loaded.
But for unit tests this is not the correct answer.
在Spring Boot中做集成测试,引入了ApplicationContext以及相应的环境,由于要初始化环境,所以会加载有点慢,除非在做集成测试,否则不要轻易使用。
By default,
@SpringBootTestdoes not start the server. If you have web endpoints that you want to test against this mock environment, you can additionally configureMockMvcas shown in the following example
默认情况,@SpringBootTest并没有启动容器,所以如果需要测试接口的话,需要额外的配置@MockMVC。
5.2 @WebMvcTest – 单元测试
To test whether Spring MVC controllers are working as expected, use the
@WebMvcTestannotation.@WebMvcTestauto-configures the Spring MVC infrastructure and limits scanned beans to@Controller,@ControllerAdvice,@JsonComponent,Converter,GenericConverter,Filter,HandlerInterceptor,WebMvcConfigurer, andHandlerMethodArgumentResolver.Regular
@Componentand@ConfigurationPropertiesbeans are not scanned when the@WebMvcTestannotation is used.@EnableConfigurationPropertiescan be used to include@ConfigurationPropertiesbeans.for testing the controller layer and you need to provide remaining dependencies required using Mock Objects.
专门用于Controller层的单元测试,进行”环境加载”的时候,只会扫描@Controller、@ControllerAdvice、Filter以及HandlerInterceptor相关的Bean。所以Controller中的其它组件需要Mock, 一般和下面的@MockMvc配合使用。
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@ActiveProfiles("test")
@WebMvcTest(value = XXController.class)
public class XXControllerUnitTest {
private MockMvc mockMvc;
}
5.3 @MockMvc
Main entry point for server-side Spring MVC test support
The MockMvc class wraps this TestDispatcherServlet internally. So every time we send a request using the perform() method, MockMvc will use the underlying TestDispatcherServlet directly.
Therefore, there are no real network connections made, and consequently, we won’t test the whole network stack while using MockMvc
提供服务器端Controller测试的相关工具,比如说输入指定的请求,看看响应是不是符合预期,主要是看Controller处理Service层的一些调用结果是不是正确。
MockMvc的局限性: 底层使用TestDispatcherServlet,不能使用整个网络栈,这句话的意思就是由于Web Server根本没有启动,底层只是调用相关类方法进行的Request Dispatch,所以正常MVC的一些流程可能无法测试到,比如说HTTP Redirection,失败之后重定向到/error页,这种就无法测试到。
5.4 @ContextConfiguration
{@code @ContextConfiguration} defines class-level metadata that is used to determine how to load and configure an {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext ApplicationContext} for integration tests.
定义类级别的元数据, 用于在集成测试中加载相应的ApplicationContext。
5.4 @TestConfiguration = Configuration in Test mode
在测试的时候,定制一些@Configuration以适应测试的需求, 比如说MybatisPlusConfig使用MySQL作为数据源,而TestMybatisPlusConfig使用内嵌数据库作为数据源。
With
@TestConfigurationwe can not only include additional beans required for tests but also override the beans already defined in the application.Read more about it in our article on Testing with
@TestConfiguration借助@TestConfiguration,我们不仅能添加测试需要的额外Bean,还能够覆盖应用中已经有的Bean
在Bean扫描时候的影响(Component Scanning Behavior), @TestConfiguration不再组件扫描之列
Though the
@TestConfigurationannotation inherits from the@Configurationannotation, the main difference is that@TestConfigurationis excluded during Spring Boot’s component scanning.
5.5 @MockBean
用来增加Mock对象,使用可以替换ApplicationContext中现有的Bean,或者是新增。在集成测试的时候,用于测试外部的服务尤其有用。
We can use the @MockBean to add mock objects to the Spring application context. The mock will replace any existing bean of the same type in the application context.
If no bean of the same type is defined, a new one will be added.
This annotation is useful in integration tests where a particular bean, like an external service, needs to be mocked.
本文主要介绍了基于Spring Boot测试的相关理论基础,下一篇《【微服务测试】基于Spring boot的微服务测试之理论篇》我们将基于一个简单的微服务案例去实践上面提到的流程。